A deep dive into opportunities in the Ethereum roadmap, DevCon, and Pectra upgrades

Reprinted from panewslab
01/13/2025·3MAuthor: HashKey Capital
Compiled by: Vernacular Blockchain

Looking back, many of the cutting-edge discussions within the Ethereum developer community have profoundly impacted the everyday applications we take for granted today, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), borrowing platforms, Rollups, and decentralized applications (dApps). These discussions often also hint at future investment opportunities.
As we head into 2025, what signals can we pick up from Ethereum’s roadmap, the recent DevCon conference, and the upcoming Pectra upgrade? Let’s find out.
1. Ethereum’s roadmap: guidance for future development
Ethereum’s roadmap has been an important reference for observing future development directions, with key milestones including The Merge, The Surge, The Scourge, The Verge, The Purge, and The Splurge. These stages illustrate Ethereum’s evolving path:
The Merge (merger phase): It mainly focuses on the combination of the execution layer and the consensus layer, completing the transition from PoW to PoS. It also includes some improvements to the consensus protocol, such as Single-Slot Finality and lowering the validator threshold.
The Surge (Expansion Phase): The core discussion revolves around future scalability improvements and underlying optimization to better support Rollups. Among them, EIP-4844 has been launched, and upcoming key features include PeerDAS (reducing node pressure) and cross-Rollup interaction capabilities.
The Scourge (cleaning phase): Mainly solves some problems related to MEV, such as the over-centralization of builders and the phenomenon that the value of MEV is captured by large-scale liquidity staking tokens (LST).
The Verge (upgrade stage): The bottom layer is converted from Merkle tree to Verkle tree, and promotes the zero-knowledge (Snarkify) of EVM.
The Purge: Reduce the storage and state maintenance pressure on Ethereum nodes by deleting or archiving historical data, while cleaning up some technical debt.
The Splurge (optimization phase): includes some more cutting-edge improvements, such as EVM underlying optimization, account abstraction, and the application of other encryption technologies (such as VDF).
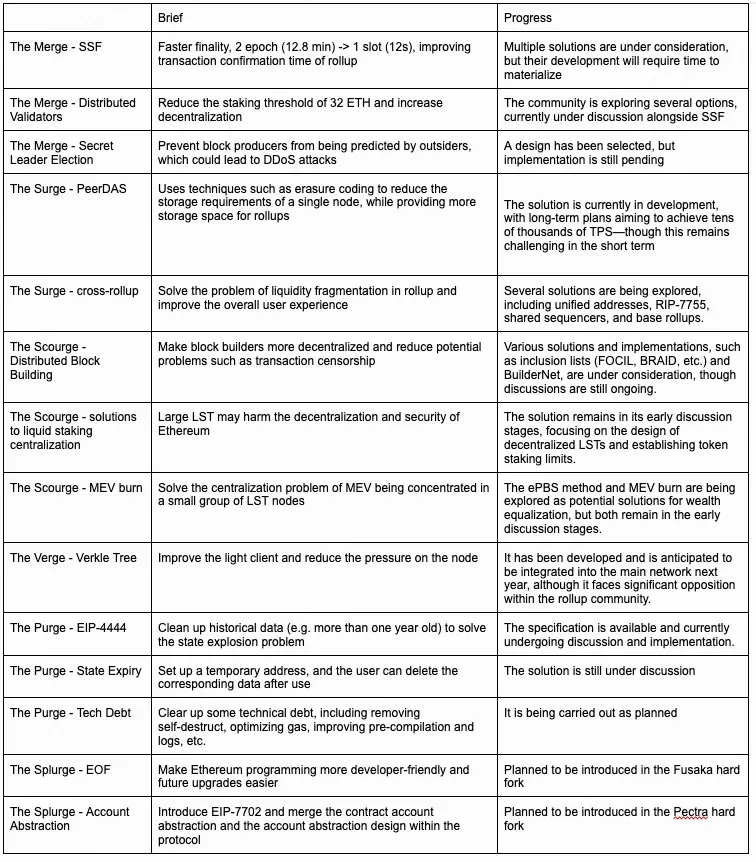
The table below summarizes the key improvements at each stage, highlighting their main impact and current progress.
By sorting out these milestones, it is not difficult to see that Ethereum’s roadmap is not only a plan for technological evolution, but also an important guide for the future development of the entire ecosystem. It both provides clear direction for developers and reveals potential opportunities for investors.
2. DevCon Conference
Another source of insights worth watching is the recent Ethereum DevCon conference, where developers and community members came together to discuss key challenges and explore innovative solutions.
One of the highlight topics was Beam Chain, a technology half-jokingly but aptly dubbed “Ethereum 3.0.” The name reflects the community's enthusiasm for exploring new directions. Beam Chain introduces some fundamental improvements, such as advancements in Snark technology, block generation, and optimization of the staking mechanism. However, since its roadmap spans roughly five years, it's more of a long-term vision than a short-term focus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gjuenkv1zrw
3. Rollup-related topics are at the core of the DevCon conference
At the DevCon conference, Rollup-related topics became the focus, among which liquidity fragmentation and Rollup interoperability were considered key issues affecting user experience. Many keynotes and panel discussions focused on potential solutions to these challenges. The conference also deeply discussed the technical maturity of Layer 2 (L2) solutions. Currently, only Optimism and Arbitrum have reached Phase 1 (permitted fraud proof), while most other L2 projects are still at Phase Zero (in centralized upgrade, no fraud proof) and require upgrades to Layer 1 (L1) Stay consistent to make progress.
The meeting also discussed chain abstraction, pre-confirmation mechanisms, cryptography applications, and future upgrade plans. The upcoming Pectra upgrade is expected to play a key role in solving these problems, which will be detailed in the next section.
4. Pectra upgrade
Pectra upgrade mainly belongs to The Surge stage, because its core goal is to improve scalability (such as Blob increase) and optimize the use of Rollup. At the same time, it also advances account abstraction and innovative features during The Splurge stage. This upgrade also partly involves storage optimization and cryptography improvements for The Purge and The Verge.
Therefore, the Pectra upgrade is a comprehensive technical update with multi-stage goals, but its focus is on scalability (The Surge) and innovation (The Splurge).
The current Ethereum Pectra upgrade is scheduled to be completed in the first quarter of 2025, and will introduce a number of important changes, covering many aspects from the underlying architecture to the end-user experience. 1) EIP-7702: Account Abstraction (AA) One of the most user-experience-focused features in the Pectra upgrade is EIP-7702. The proposal builds on the concepts of EIP-3074 and EIP-4337 and allows all external accounts (EOA) to be temporarily converted to smart contract accounts. This upgrade will simplify the user experience, such as enabling single-signature multi-transaction processing and zero gas fees. However, this may also introduce certain security risks, such as signature phishing. Therefore, wallets and related products need to be upgraded accordingly to adapt to this change. Overall, EIP-7702 is expected to provide great opportunities for account abstraction projects. See our related report for more details. 2) EIP-7691: Increase the number of blobs The Pectra upgrade will adjust the number of blobs per block, increasing the target value from 3 to 6 and the maximum value from 6 to 9. Blob provides a more economical storage method for Rollup. This improvement will reduce the cost of Rollup and improve the competitiveness of Ethereum decentralized applications (dApp). While this change will slightly increase the operating costs of the nodes, it will significantly improve storage efficiency, giving Rollup greater advantages. Additionally, this adjustment will result in a faster gas charge decrease (when the blob is not used) and a slower gas charge increase (when the blob reaches full capacity). 3) EIP-7251: Increase the staking limit The Pectra upgrade also increases the staking limit of Ethereum from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH. This change allows staking service providers and large holders (whales) to consolidate their ETH into a single node, thereby reducing the number of validators and making the staking process more efficient.
The Pectra upgrade not only represents an important technological breakthrough for Ethereum, but also demonstrates its all-round improvements in user experience, scalability and efficiency, injecting more potential into the future development of the ecosystem.
5. Future opportunities
The Ethereum ecosystem’s ongoing technological advancements and research discussions bring exciting possibilities for its future development. Here are some of the key opportunities shaping the future. 1) Interoperability between Rollups In discussions on the Ethereum roadmap and DevCon, a recurring theme is enhancing the liquidity and interoperability between Layer 2 (L2) Rollups. Solving these problems is critical to improving user experience and scaling Ethereum.
Solutions currently under development:
Rollup based on Layer 1: Currently, many L2s use a centralized sequencer (Sequencer) to sequence transactions and publish them to Layer 1 (L1), which limits the timely interaction between L2s. One proposed solution is to use L1 as the ordering layer, thus ensuring atomic interactions between L2 using this approach.
Shared sequencers: Another approach is for multiple L2s to share a common set of sequencers, facilitating seamless interactions and reducing liquidity fragmentation.
Cross-Chain Intents: In addition to sequencers, cross-chain intents allow developers to solve interoperability issues at a higher level and support coordinated interactions between Rollups.
Progress and Key Players: The Ethereum community is actively developing and testing solutions to these challenges:
Spire Labs' Based Stack: Designed specifically for L1-based Rollup, expected to be online in the first quarter of 2025.
Shared Sequencer Project: Platforms such as Astria, Espresso and Polygon AggLayer are iteratively developing shared sequencer models.
ERC standard:
ERC-7683: Supported by Unichain, Arbitrum, etc., designed to solve cross-chain liquidity issues.
Optimism's ERC-7802: Superchain ERC20 is introduced to provide a unified asset standard within the superchain ecosystem and promote liquidity transfer.
As these solutions evolve, they may compete for dominance in 2025, reshaping Rollup's interoperability and Ethereum's scalability. 2) The activation of Account Abstraction (AA) EIP-7702 will affect all External Account (EOA) addresses, creating significant opportunities for the Account Abstraction (AA) project. Combined with advances in chain abstractions, intents, and related technologies, EIP-7702 is expected to drive the development of more complex cross-chain and multi-chain interaction capabilities.
However, the AA track is at a critical moment, after previous market performance of standards such as ERC-4337 was unsatisfactory. The upcoming Q1 2025 Pectra upgrade may be the last big opportunity for the AA ecosystem to achieve product-market fit. Teams like Zerodev that are the first to adopt EIP-7702 are expected to take full advantage of this upgrade and may experience significant growth. Future results will soon be apparent. 3) Cryptozoology Applications Cryptography has always been at the core of the Ethereum roadmap and DevCon discussions, and its advancements are paving the way for breakthrough technologies and applications.
Technical level: Frameworks such as zkEVM and zkVM are continuing to mature, and combined with the application of technologies such as zero-knowledge proof (ZKP), multi-party computation (MPC) and fully homomorphic encryption (FHE), they show the potential for innovation. Cutting-edge technologies such as indistinguishable obfuscation (iO) were specifically mentioned in the DevCon discussion. This technology, known as the "crown jewel" of cryptography, may gain more attention in the near future.
Consumer side: There is huge potential in cryptographic advances. For example, applications such as ZK Email (represented by the Aztec Noir implementation) and zkTLS may be more widely adopted, providing users with higher security and privacy protection. In addition, the recent rejection of OFAC sanctions against Tornado Cash has alleviated compliance concerns about privacy technologies to a certain extent and may accelerate the acceptance and use of these technologies in real-world applications.


 chaincatcher
chaincatcher