Eight months after PBS was fully implemented, how is the BNB chain performing?

Reprinted from panewslab
01/16/2025·18days agoBNB Smart Chain implemented BEP 322 (Proposer-Builder Separation Mechanism PBS) this year, which brought a series of ecological changes on the chain and gave birth to risks and opportunities.
BSC chain verifiers have a higher position in the ecological chain and have the right to speak ecologically on the BSC chain. The entry threshold for BSC verifiers is high, and the number of verifiers has remained at 40+ for a long time. Compared with Ethereum's million-level verifier nodes, BSC verifiers have a stronger influence on the on-chain ecology.
After the implementation of PBS, the Builder market formed a head-waist-tail pattern. The top players in the Builder market, Blockrazor and 48Club-pussaint, contributed nearly 80% of the block construction, while Bloxroute, Blocksmith and Nodereal contributed about 19% of the block construction. The tail players only contributed sporadic block construction. In addition, the vertical integration phenomenon of Validator-Builder on the BSC chain may further cause centralization risks.
The new mechanism gave rise to on-chain transaction risks and the formation of risk prevention products. BSC’s unique 0Gwei trading mechanism reduces transaction costs and causes frequent phishing activities on the chain. Under the PBS mechanism, the mechanism for Builder to receive transaction bundles reduces the cost of sandwich attacks, making transactions more susceptible to sandwich attacks, giving rise to the formation of MEV-resistant privacy RPC products.
Research background
BNB Smart Chain implemented BEP 322 (Proposer-Builder Separation Mechanism PBS) this year. This is a major update of the BSC chain ecological mechanism, giving birth to the BSC Builder market and bringing some new ecological gameplay. We hope to start from the mechanism of BEP 322, by studying the similarities and differences between BSC PBS and Ethereum PBS mechanisms, the development of Builder and Validator, etc., and describe the implementation of BEP 322 from multiple perspectives such as the underlying mechanism and ecological performance, as well as the Some possible on-chain security risks may be hidden, and we will provide our users with suggestions on how to deal with security risks.
Differences between BSC and Ethereum PBS mechanisms
Regarding the PBS mechanism, BSC follows most of the implementation mechanisms of Ethereum. However, considering that BSC has certain differences from Ethereum in terms of consensus mechanism, validator network topology and other factors, there are some detailed differences between BSC and Ethereum in the implementation of the PBS mechanism. :
① The Relay mechanism is cancelled: Due to the small number of BSC validators, there is no need for a centralized Relay to reduce the complexity of communication between Builder and Validator, and considering that the interval between each block of BSC is short, Relay forwards transactions On the contrary, this method will increase the communication link between Builder and Validator and increase the interaction time. As a supplement to Relay, BSC introduces the mev-sentry service. Each validator runs its own sentry, and the sentry service directly interacts with the Builder. This sentry-Validator separation mechanism can better protect the validators. At the same time, unlike Relay, Validator can directly obtain the block content of Builder bid through sentry, and validators can verify the validity of Builder bid by themselves, which can also further protect the interests of validators. In addition, in each block interval, the Builder can only send no more than 3 bids to sentry, which also leads to a large difference in the bidding strategies of BSC Builder and Ethereum Builder.
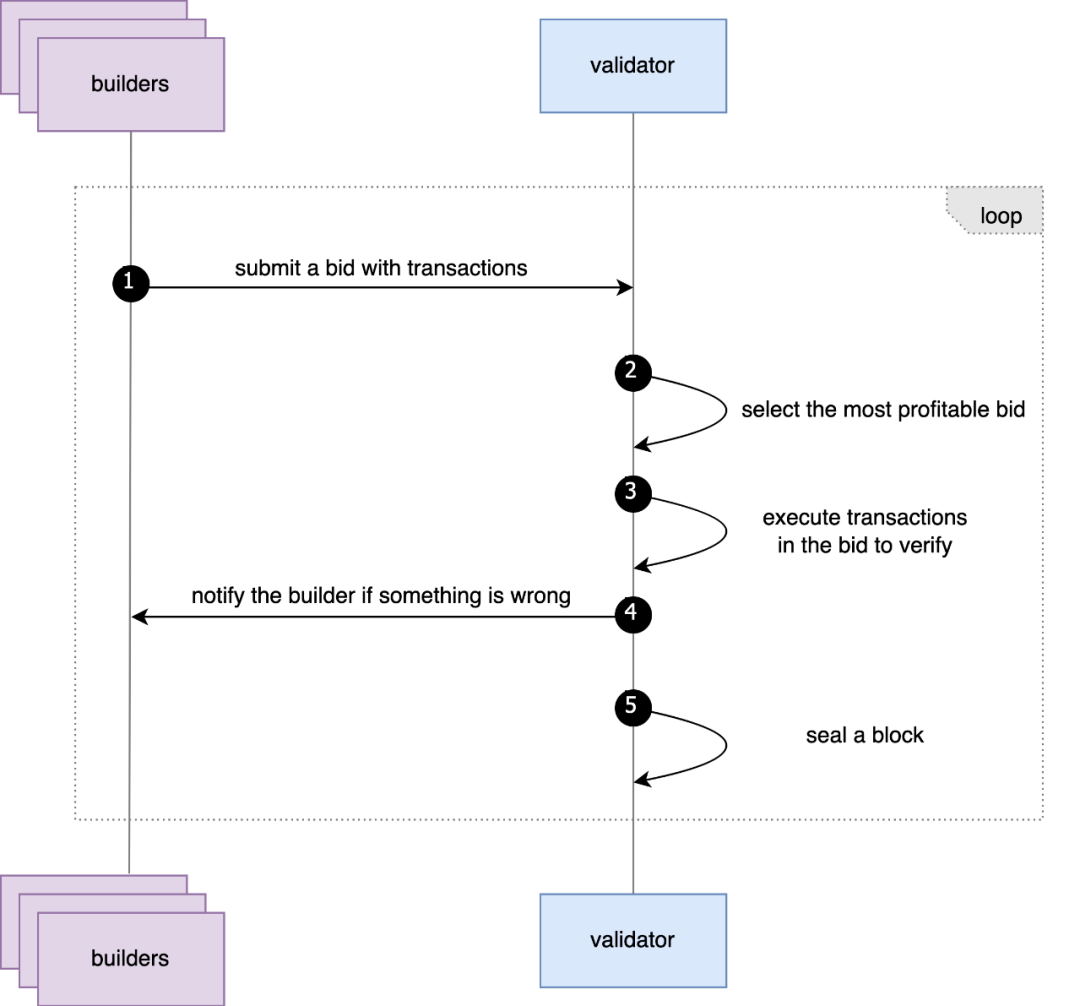
② Differences in Coinbase transfer settings: Ethereum’s PBS mechanism allows the Builder to change coinbase to the Builder’s own address. This mechanism allows Ethereum’s priority fee to be redistributed once by the Builder, while BSC’s PBS mechanism does not have the above capabilities. This To a certain extent, it limits the Builder’s bidding allocation capabilities.
③ 0Gwei transaction support: Before the BEP-322 upgrade, the 0Gwei mechanism was first introduced by 48Club. This mechanism was launched as a member feature of 48Club. It can be used by holding the 48 member token KOGE and meeting certain conditions. It is an added value provided by the verifier. Serve. After the BEP-322 upgrade, BSC validators are allowed to receive blocks with 0Gwei transactions. Different from the Ethereum dynamic Base Fee mechanism, the transaction Base Fee of the BSC chain defaults to 0, that is, transactions with a Gas Price of 0 are allowed. As a supplement to the minimum GasFee guarantee mechanism, the BSC chain sets a limit that the Effective Gas Price of the block cannot be lower than 1. This special mechanism allows the Builder to include transactions with a Gas Price of 0 when building a block, so that the block space can be more fully utilized.
Builder market development
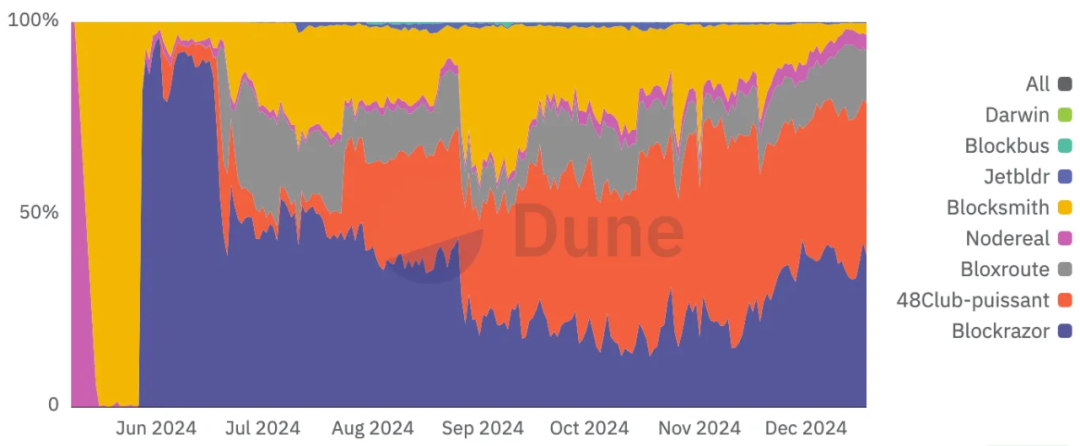
Similar to Ethereum, after the implementation of PBS, the Builder market was formed and experienced a period of development, eventually forming a head-waist-tail pattern.
According to statistics provided by Dune, a total of 8 Builder players participated in the BSC Builder market game. In the early days of PBS implementation, Nodereal, Blocksmith and Blockrazor all briefly dominated the entire market. With 48Club and Bloxroute joining the game at the end of June, the market began to enter a tug of war. Up to now, Blockrazor and 48Club have contracted more than 80% of the block construction on the entire BSC, becoming the leading players in the Builder market. Bloxroute, Blocksmith and Nodereal have become waist players, while Jetbldr, Blockbus and Darwin only have sporadic numbers. of blocks.
Validator development
Unlike Ethereum, due to different entry barriers, the number of validators on BSC has always been maintained in a stable range.
On Ethereum, you only need to pledge 32 ETH to become a validator, which makes the number of validators on Ethereum exceed 1 million. The validators connect to the Builder through integrated Relay, obtain the builder's block proposal and complete the block generation.
On BSC, becoming a validator requires staking a large amount of BNB, which greatly increases the entry threshold for validators. Currently, there are only 45 validators on BSC, of which 21 are Cabinet and the remaining 24 are Candidate. According to BSCScan statistics, 45 validators have pledged a total of 29,244,219 BNB, and the validator with the least pledge has pledged 73,446 BNB.
The difference in the concentration of validators has to some extent led to the ecological differences between BSC and Ethereum. For example, on BSC, due to the lower link cost between Builder and Validator, there is no market space for Relay services. At the same time, the influence of verifiers causes the development of the on-chain ecology to prioritize the interests of verifiers, which will affect the competitiveness and enthusiasm of project parties other than the verifier group in the public chain co-construction ecosystem.
Potential risks on the chain
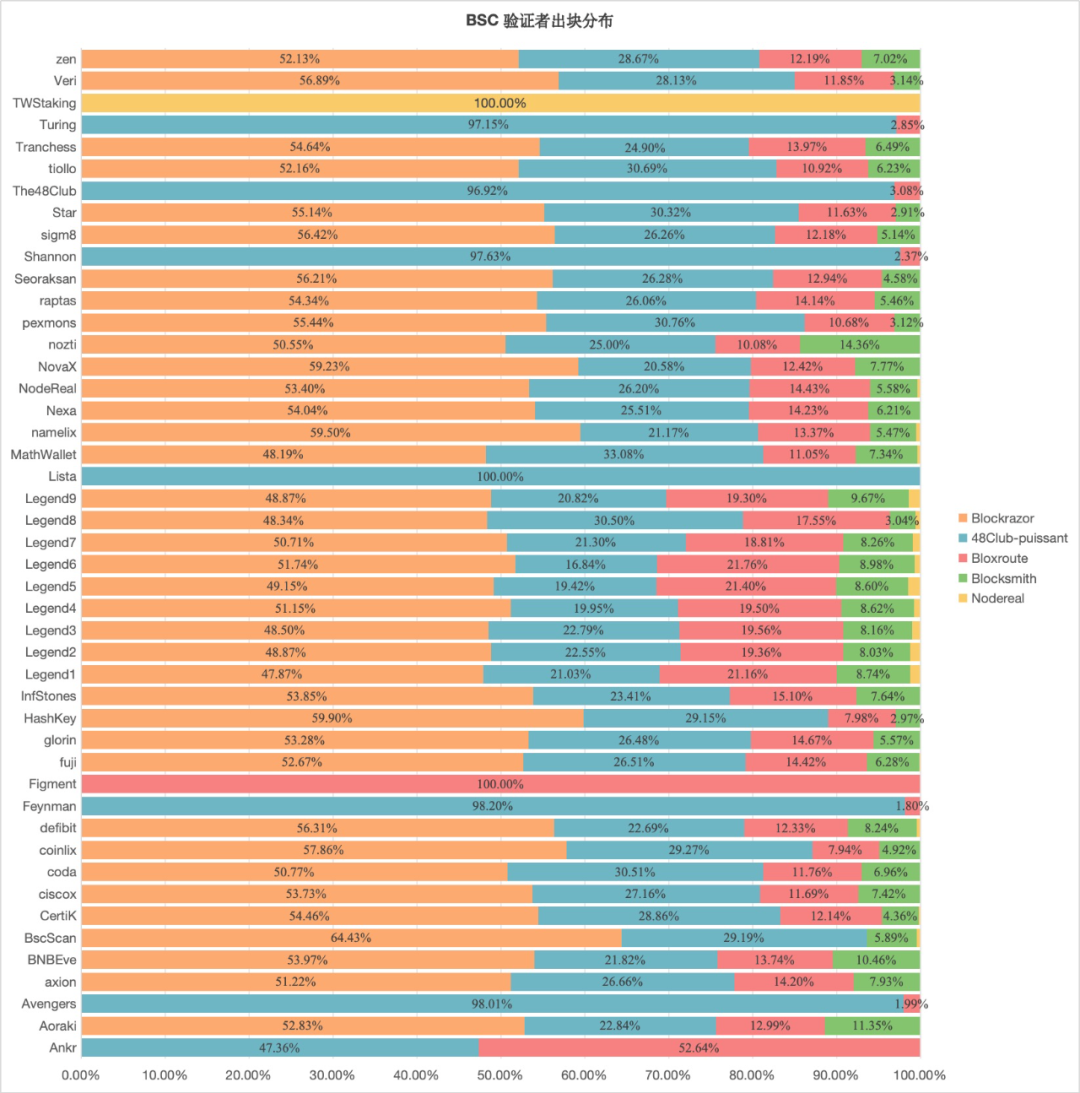
There is a significant Builder-Validator vertical integration phenomenon on BSC. We made statistics on the distribution of Builder blocks among all Validators from 00:00:00 on December 1st to 00:00:00 on December 18th. The block production situation of some validator nodes significantly deviated from the market. The average value indicates the vertical integration between Builder-Validator. (Nodereal’s share in TWStaking is 100%, Bloxroute’s share in Figment is 100%, 48Club’s share in Turing, The48Club, Shannon, Lista, Feynman, and Avengers is >90%). The potential risks brought by this vertical integration are different from the common Searcher-Builder integration on Ethereum. There is the possibility of using the Builder-Validator integration mechanism to control the flow of transactions and transmit transactions only to specific validators, which will cause loss of user interests and Risks of further centralization.
0Gwei’s trading mechanism has room to be exploited by phishing contracts. 0Gwei transactions enable phishing contracts to transfer funds at 0 cost, exacerbating the rampant nature of phishing attackers. We have detected multiple 0Gwei phishing contracts on BSC that initially used 48Club’s 0Gwei transactions to hold 48Koge tokens. , although 48Club has placed certain restrictions on this, as of press time, we have still observed several phishing operations conducted through the 48Club 0Gwei trading service.
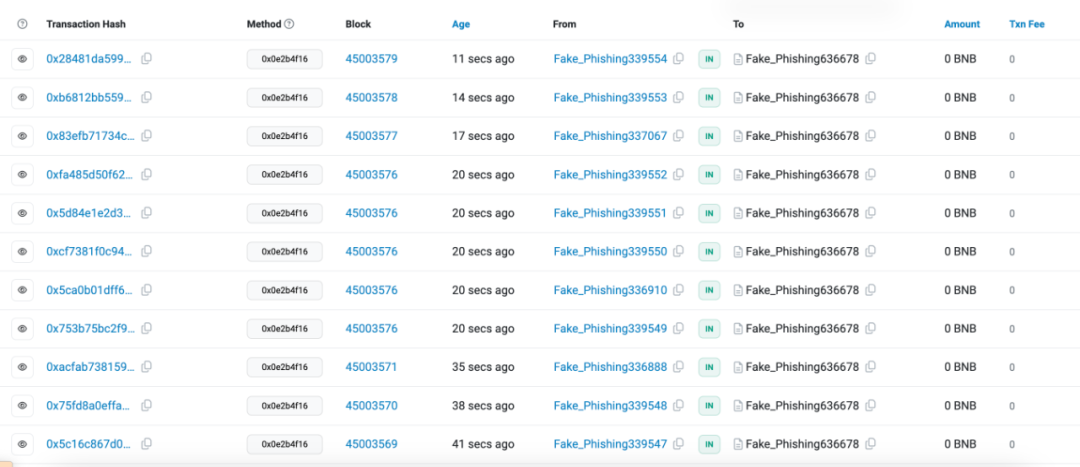
How to avoid various phishing attacks and track lost assets, related reading: https://blocksec.com/blog/how-phishing-websites-bypass-wallet-security-alerts-strategies-unveiled)
The current PBS mechanism has shuffled the MEV attack market, and users need to master MEV protection methods under the new pattern. Sandwich Attack is the most notorious MEV attack on the current blockchain. The principle of sandwich attack is:
- Monitoring of target transactions: The attacker monitors the transaction pool (mempool) on the blockchain to look for target transactions. The target is usually a large token exchange transaction (such as exchanging ETH for USDT in a DEX).
- Front-running: The attacker sends a transaction (front-running transaction) before the target transaction in order to affect the market price before the target transaction is executed. For example, the attacker purchases the target token, thus driving up the price.
- Back-running: After the target transaction is executed, the attacker sends a transaction in the opposite direction (back-running transaction) to sell the tokens in the previous transaction and profit from the price fluctuation caused by the target transaction. .
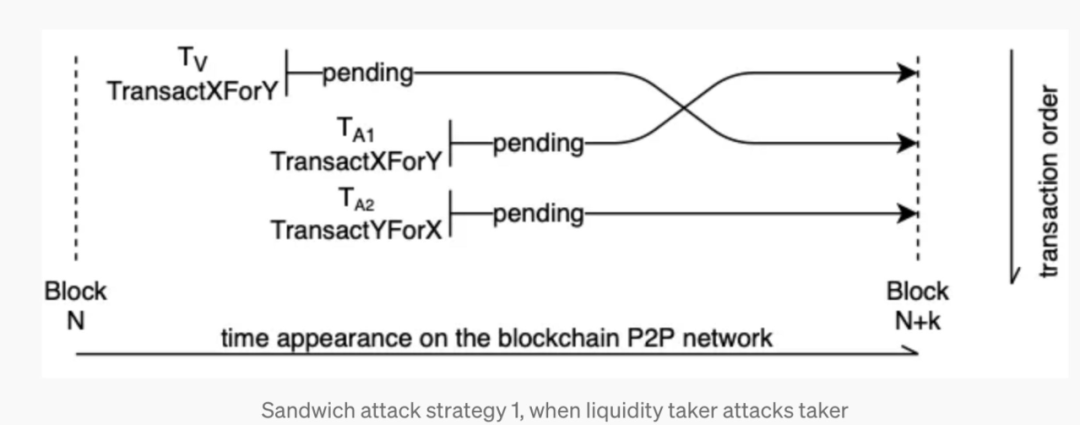
To learn more about MEV background knowledge, related reading: https://blocksec.com/blog/harvesting-mev-bots-by-exploiting-vulnerabilities-in-flashbots-relay
Before PBS, transactions were in the public transaction pool and were completely exposed to the attacker's view. The attacker could analyze all profitable transactions and control the order of transactions by controlling the gas price to complete the attack.
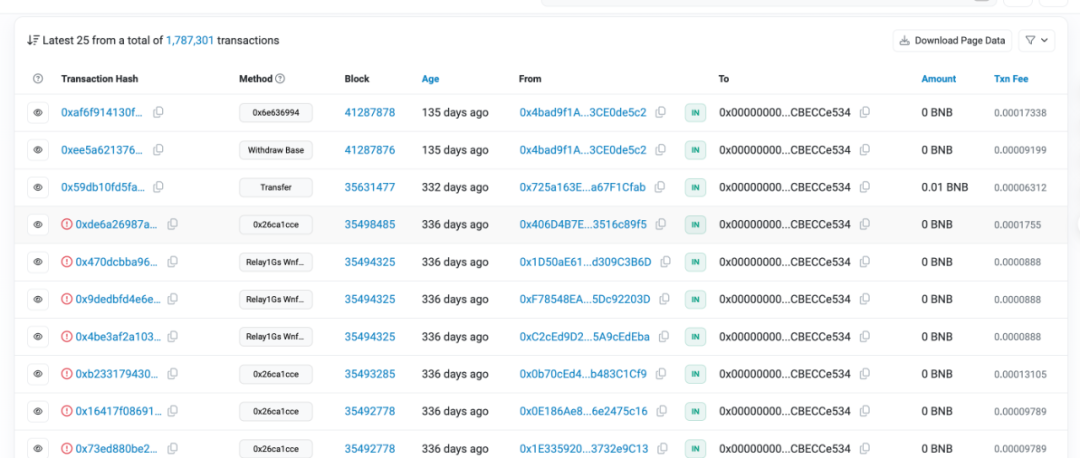
The PBS mechanism provides a private channel for transactions, which can send user transactions to a private transaction pool visible only to the Builder, ensuring that the transaction will not be discovered by attackers (unless the Builder intentionally leaks it), thereby protecting user transactions. We found that the head sandwich bot (0x00000000004e660d7929B04626BbF28CBECCe534), which once conducted sandwich attacks by controlling gas prices, was completely shut down more than 100 days ago, indicating that the PBS mechanism of BSC has caused a reshuffle of the MEV attack pattern.
However, by observing on-chain behavior and analyzing statistical data (https://dune.com/hildobby/sandwiches?Blockchain_e8f77a=bnb), we found that after PBSization (May 2024), the number of transactions of sandwich attacks on the BSC chain has actually increased. significantly increased.
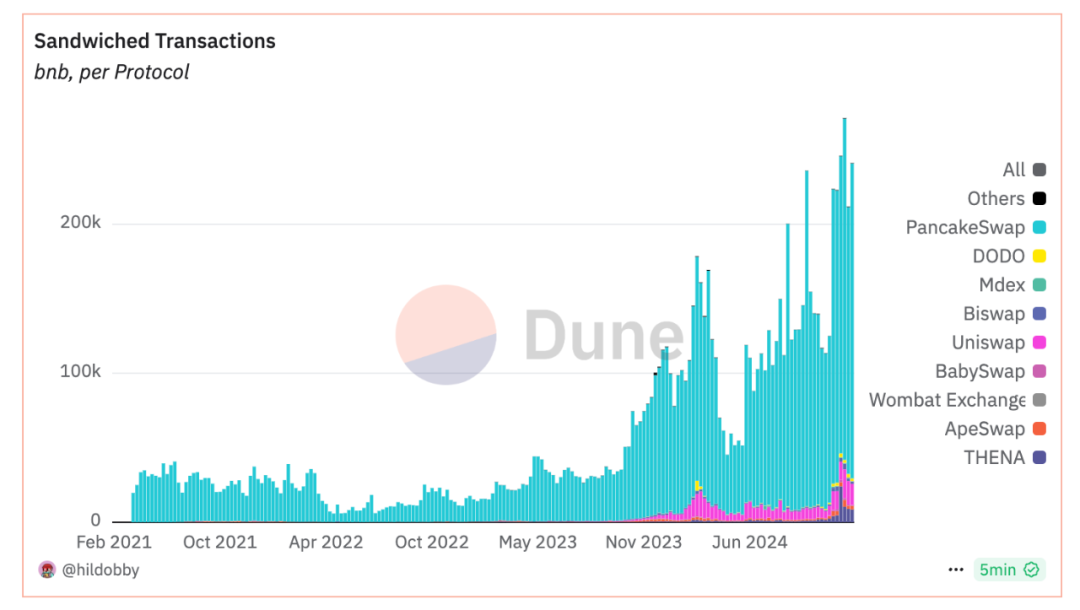
The main reason is that most traders and project parties do not make good use of the transaction privacy channel brought by PBS, and still send transactions to the public transaction pool. For attackers, the cost of obtaining attack opportunities is not significant. improve. On the contrary, the attacker uses the mechanism that the Builder can accept the Bundle, and submits the attacked transaction and the attacking transaction together to form a Bundle and submits it to the Builder. If the Bundle is successfully uploaded to the chain, the sandwich attack is successful. If it is not successfully uploaded to the chain, the Seacher will not bear any consequences. losses, which makes sandwich attacks more cost-effective and effective.
In the new environment after BSC PBS, new methods need to be adopted to deal with the increasingly rampant and diverse MEV attacks.


 jinse
jinse
 chaincatcher
chaincatcher