U card is becoming more popular, but what are the potential tax and legal risks?

Reprinted from panewslab
02/11/2025·2DAuthor: FinTax
introduction
In recent years, with the rapid development of cryptocurrency market and digital payment technology, some exchanges, wallet service providers, etc. have successively launched their own U card products, and U card has become more and more Web3 users to conduct cross-border payments and daily consumption. tools. At the same time, discussions on U cards on various social media platforms have also shown explosive growth, and U cards have become the focus of hot discussion. Some see it as the key to solving the cryptocurrency OTC problem, some are waiting and watching, and some are full of doubts about it. FinTax will introduce you to the basics of U cards in this article and specifically remind you that you should not ignore the tax and other risks hidden by U cards.
1. The concept of U card
1.1 U card
U cards are a tool that provides financial services to cryptocurrency investors. The U card is used similarly to a bank card. Cardholders can directly consume or withdraw cash through the U card, and do not need to convert virtual currencies into fiat currency in advance.
U cards are divided into two categories: physical U cards and virtual U cards. Physical U cards such as Mastercard, UnionPay U cards, etc. have a wider range of acceptance and higher acceptance. Virtual U cards such as Dupay are mostly used in e-commerce or international payments, which are more convenient and flexible, but cannot be used for cash withdrawal operations on the ATM.
Common U card issuance modes include the following:
- Direct issuance by the bank. Banks use their own payment network and compliance framework to provide users with stable cryptocurrency payment solutions.
- Banks cooperate with cryptocurrency companies to issue. At this time, the bank provides traditional financial infrastructure, while third-party companies are responsible for the management and conversion of cryptocurrencies.
- Professional crypto payment company issuance independently. Some companies focusing on cryptocurrency payments independently issue U cards by partnering with payment networks such as Visa or MasterCard.
- SaaS model issuance. This refers to some third-party payment companies providing U card issuance platforms for channel vendors or other financial service providers through the SaaS (Software as a Service) model.
1.2 U card usage mechanism
U cards are more convenient to use, which is one of the important reasons why they are widely accepted. We can understand the usage mechanism of U cards in two steps.
- Recharge: The user recharges USDT into the wallet, and then recharges USDT from the wallet address into the U card address. At this time, the U card operator will settle the USDT into the corresponding foreign currency.
- Withdrawal or consumption: Users can use U cards to withdraw cash from ATMs around the world, or they can directly swipe U cards to pay for the fee. At this time, what they pay is already redeemed fiat currency, not USDT.
2. Reasons for U cards to be popular
2.1 Protect personal privacy
Web3 users often pay more attention to personal privacy, including transaction privacy, and hope to remain anonymous when making payments or transfers, while U cards provide users with excellent privacy protection mechanisms. On the one hand, virtual U cards usually do not require real-name registration, allowing users to purchase or recharge anonymously; on the other hand, although physical U cards may require a certain level of KYC certification, it is compared to the large number of individuals that need to be provided when conducting transactions through traditional banks. Information, U cards still greatly reduce the risk of personal information exposure.
2.2 Simplify payment process
U cards can usually provide real-time payment and settlement, which not only avoids the possible time delay of traditional bank transfers, but also does not need to convert USDT into fiat currency separately before use, which is highly convenient. At the same time, in addition to traditional POS payment, U cards can also be paid through digital wallets, scanning code payment, etc., which is compatible with various mainstream payment channels and has strong flexibility.
2.3 Reduce cross-border payment costs
The handling fees of U cards are often significantly lower than those of traditional payment channels, which is particularly obvious in cross-border payments. The following is a comparison of cross-border handling fees for multiple payment methods:
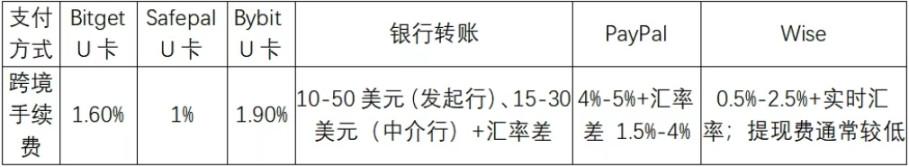
3. Potential risks of U cards
3.1 Tax risk
Due to the support of anonymous or less real-name requirements, some users want to avoid taxes through U cards, such as using U cards to conceal income sources, thereby reducing tax payable. However, this kind of tax avoidance through U cards is actually not feasible. First of all, although U cards have a certain degree of anonymity, most U cards still rely on international payment networks (Visa, Mastercard, etc.). These payment networks will record the data of each transaction in detail, including transaction amount, merchant information, transaction time, etc. Therefore, the tax authorities can actually still track the flow of relevant funds through these transaction records. Secondly, for cross-border transactions, tax authorities can also track cross-border capital flows through foreign exchange monitoring systems, bank information exchange and other means. Many countries have signed the automatic tax information exchange agreement (CRS, Common Reporting Standard), and cross-border capital flows are relatively transparent. In this way, the tax authorities can also obtain transaction information related to the U card. Finally, in actual use, payment platforms may also conduct strict real-name reviews on large-value transactions. If users are involved in frequent large amounts of capital flows, the platform may require additional information such as proof of the legitimacy of the source of funds. Therefore, tax avoidance through U cards is not actually feasible and may also incur tax audits and penalties.
3.2 Legal risks
There are also several legal risks to be paid attention to when using U cards. For example, in some countries with strict foreign exchange management, although the U card does not set an upper limit for personal deposit and withdrawal of U, the exit behavior of funds exceeding the foreign exchange quota will also affect foreign exchange management regulations. If it is discovered by the foreign exchange management authority, it will be punished. Administrative fines, even crimes. For example, the legal status of cryptocurrencies in some countries is not yet clear, and some countries completely prohibit the use of cryptocurrencies. At this point, using a cryptocurrency U card to conduct transactions may also be considered illegal. Therefore, before using a U card, users should understand the basic compliance requirements of their country and region. In addition, users should not use U cards as a tool for illegal crimes. For example, if a user uses a U card to conduct high-frequency, large-scale transactions, or helps others cash out, it will also be considered illegal business or money laundering activities and face criminal penalties.
4. Conclusion
In short, U Card has provided an excellent off-chain payment solution for cryptocurrency investors with its strong privacy, convenient payment and low handling fees, and has won many favors. However, U cards are not perfect, and U cards users still face potential problems such as tax risks and legal risks, and must be treated with caution, otherwise the gain will not be worth the loss.
 jinse
jinse

 chaincatcher
chaincatcher